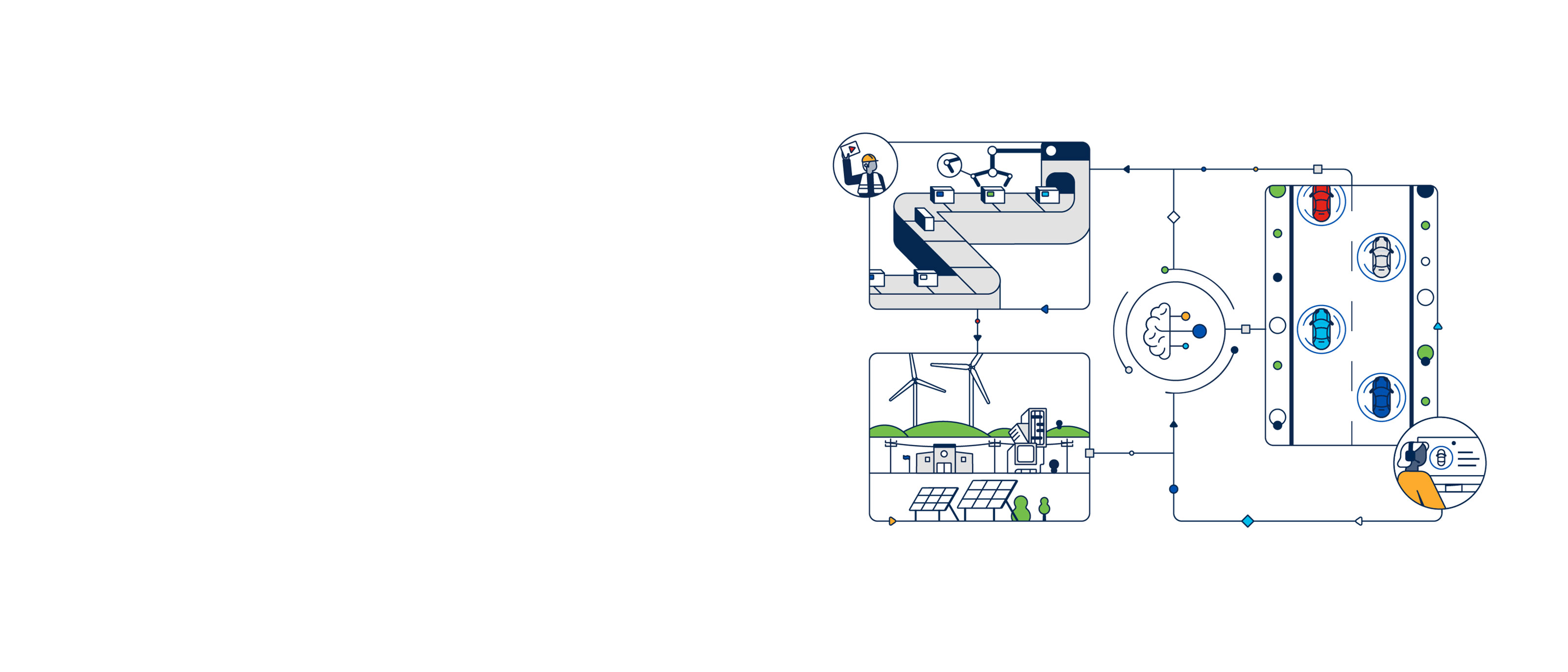
What's the origin of Industry 4.0?
The term "Industry 4.0" was coined by German scientists developing a high-tech strategy for the German government in 2011. It refers to the current phase of industrial development, in which machines can communicate and collaborate with one another and with business processes and IT in ways that make industrial processes more efficient, flexible, and responsive to business needs.
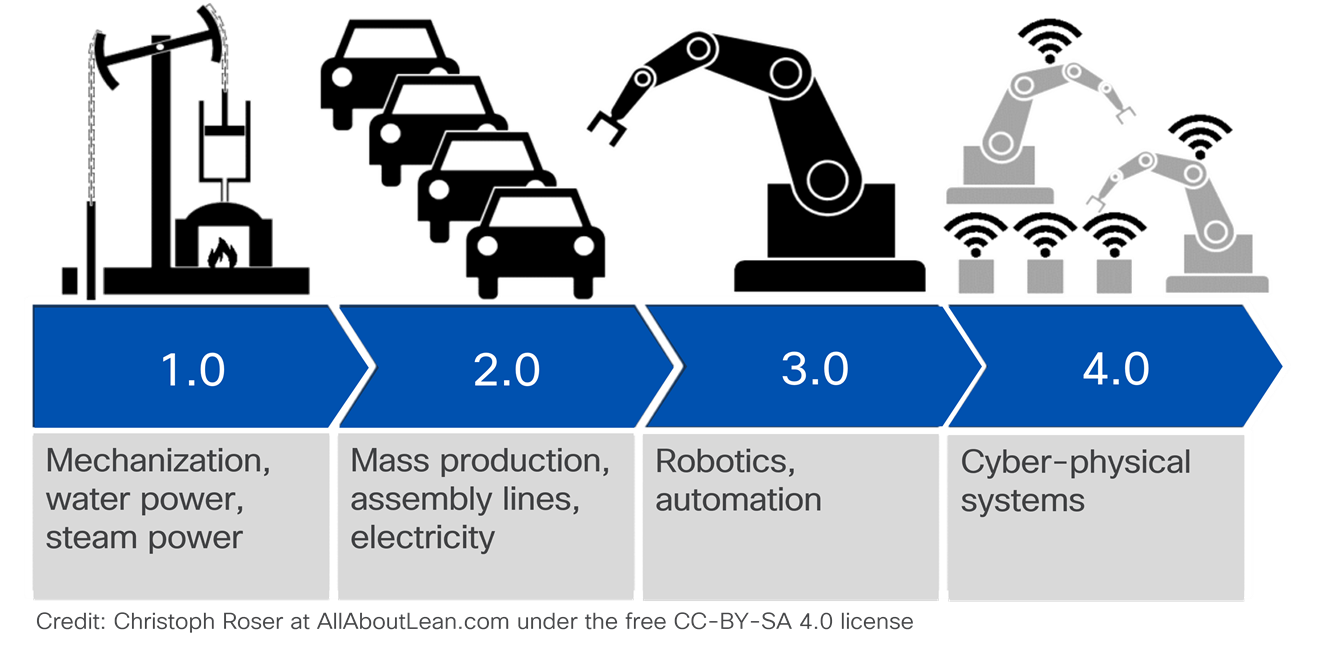
Industry 4.0 follows Industry 3.0 (robotics and automation), Industry 2.0 (assembly lines and mass production), and Industry 1.0 (mechanization of human labor).